I
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Incident Response
- Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Industry 4.0
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Infrastructure Security
- Innovation Product Design
- Innovation Product Development
- Insider Threat Detection
- Integration Testing
- Intelligent Automation
- Intelligent Process Automation
- Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Internet of Things Platform
- Internet of Things Strategy
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
- IT/OT Convergence
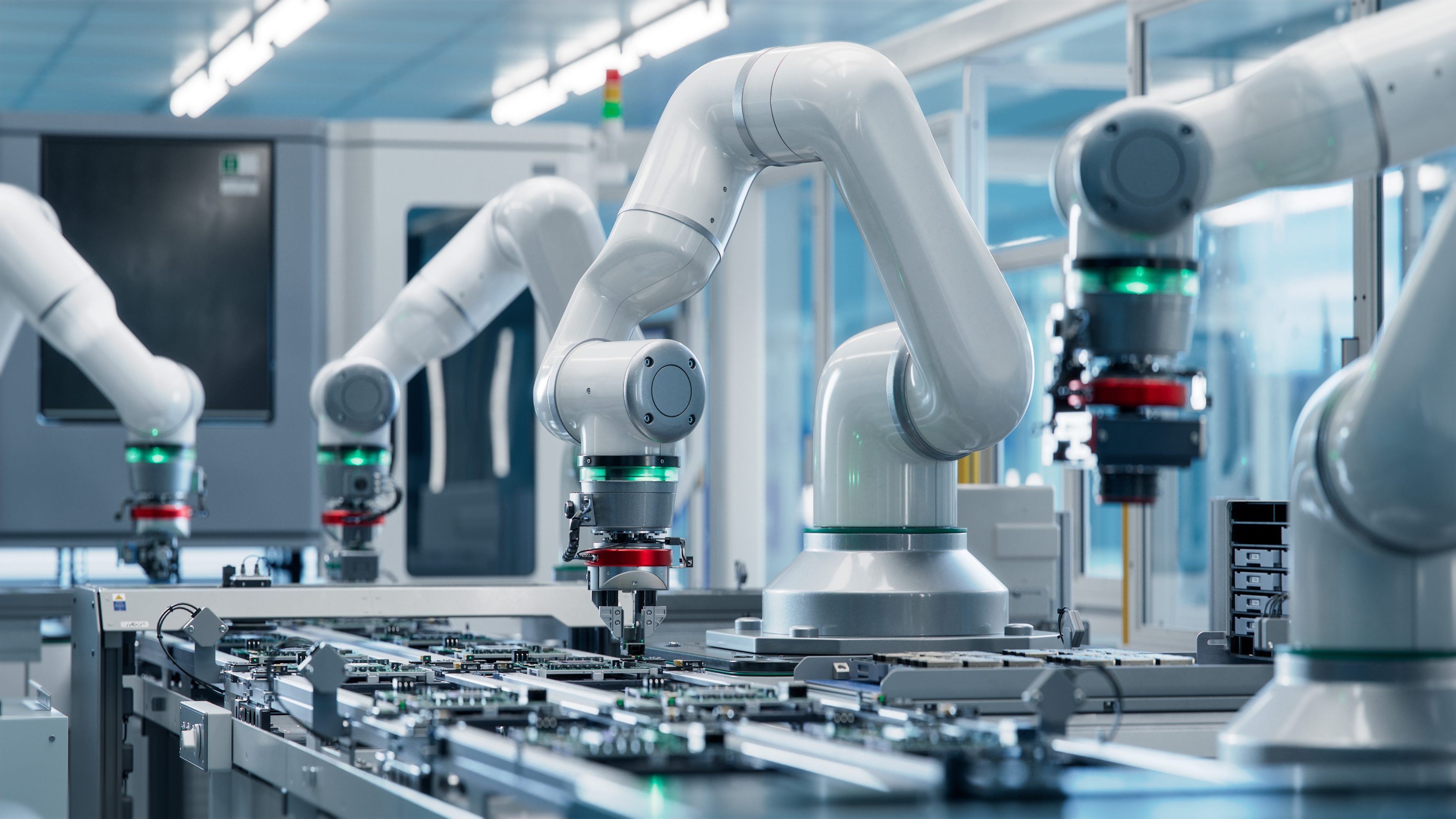
Smart Manufacturing
Simple Definition for Beginners:
Smart manufacturing refers to the use of advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making in manufacturing industries.
Common Use Example:
A factory implements smart manufacturing technologies to automate production lines, monitor equipment health in real time, and analyze data for predictive maintenance.
Technical Definition for Professionals:
Smart manufacturing integrates digital technologies and data analytics throughout the manufacturing lifecycle to achieve greater agility, flexibility, and productivity. It involves leveraging IoT devices, sensors, AI-driven analytics, robotics, and automation to connect machines, systems, and processes. Smart manufacturing enables real-time monitoring and control of production operations, predictive maintenance, quality assurance, supply chain optimization, and continuous process improvement. Key components include digital twins, industrial IoT platforms, data-driven decision support systems, and interconnected networks that facilitate seamless communication and collaboration across the manufacturing ecosystem.
Smart Manufacturing