D
- Data Analytics
- Data Loss Prevention
- Data Migration
- Data Platform
- Data Privacy
- Data Science
- Data Transformation
- Deep Learning
- Definition of Protocol Analysis | OrangeMantra
- Denial of Service (DoS)
- Dependency Scanning
- DevOps
- DevSecOps Pipeline
- Digital Engineering
- Digital Forensics
- Digital Transformation
- Disaster Recovery
- Distributed Version Control System (DVCS)
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
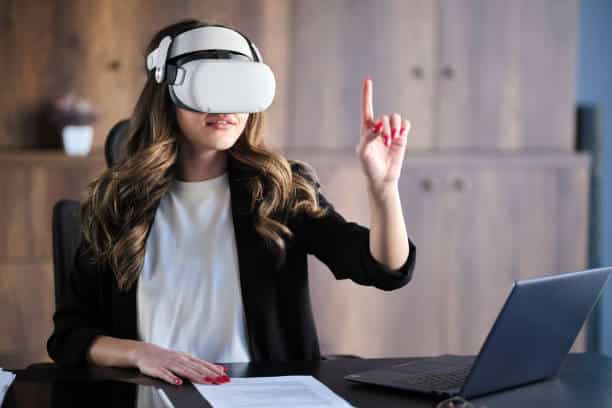
Virtual Reality (VR)
Simple Definition for Beginners:
Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that creates immersive, computer-generated environments or simulations, allowing users to interact and experience a virtual world as if they were physically present.
Common Use Example:
A person wears a VR headset to explore a virtual museum, where they can walk around, examine artifacts, and learn about history through interactive exhibits.
Technical Definition for Professionals:
Virtual reality (VR) refers to a simulated environment or experience created using computer technology and specialized hardware, such as VR headsets or goggles. VR environments can be entirely computer-generated or based on real-world environments captured through 360-degree videos or photographs. Users interact with VR environments using motion controllers, hand tracking, and other input devices to navigate, manipulate objects, and engage with virtual elements. VR technology relies on techniques like 3D rendering, spatial audio, haptic feedback, and immersive displays to create a sense of presence and realism, allowing users to suspend disbelief and feel fully immersed in the virtual world.
Virtual Reality (VR)