Learn how fuzz testing finds hidden software flaws before attackers do. This guide covers modern fuzz testing methods, real tools, and where teams use it in 2026.
Here's What You’ll Learn
- What fuzz testing is and how it exposes crashes, memory leaks, and security bugs
- Key fuzz testing types, black box, white box, and gray box, with use cases
- Popular fuzz testing tools teams use in 2026
- How to add fuzz testing to your QA and DevSecOps workflow for faster, safer releases
Crashing incidents are becoming more common because modern software is no longer simple. It runs across microservices, APIs, cloud layers, and third party integrations.
Your application is interacting with thousands of inputs you did not design for. Traditional and manual testing is strong. But it cannot always predict how software behaves when it receives unusual or malformed data.
Fuzz testing gives businesses a way to catch deeply hidden bugs before they reach customers. It stress tests your software with millions of unexpected inputs that no manual tester or scripted test case can think of.
In the last few years, fuzz testing has moved from being a niche security practice to a serious business priority. Businesses are adding it to their quality engineering playbook because the cost of a missed vulnerability is rising fast.
This guide explains what is fuzz testing, how it works, the tools used by modern engineering teams, and when your business should consider it.
Table of Contents
What is Fuzz Testing?
Fuzz testing is a software testing method where a system is tested with unexpected, random, or intentionally broken inputs to see how it behaves. Instead of giving the application clean and predictable data, fuzz testing throws unusual values, strange characters, oversized files, and corrupted payloads that real users or attackers might trigger.
In simple words, fuzz testing is like stress testing your software’s input handling. You are asking a very basic question.
What happens when something unpredictable enters your system?
For most businesses, this is where traditional testing starts to fall short. Because real production traffic is messy. Users click in strange patterns and third party systems behave differently under load.
Fuzz testing helps you discover how your system handles all this chaos. All these problems may look small, but they can trigger major incidents when the software scales or faces real-world traffic.
The business impact is significant. A single fuzzing session can reveal a vulnerability that might otherwise slip into production. Preventing that failure saves hours of debugging, avoids customer escalations, and protects your reputation.
How Fuzz Testing Works?
Here is the process broken down in a way that is easy to understand how fuzz testing really works.
Step 1: Prepare the Target
The first step is to decide what part of your application you want to test. It could be an API endpoint, a file uploader, a payment workflow, or a microservice that processes user data. The target should be clear, isolated, and easy to monitor.
Step 2: Generate Unexpected Inputs
This is where fuzzing gets powerful. The fuzzer (an automated software testing tool) creates a huge variety of inputs.
Some are random. Some are mutated versions of valid data. Some are intentionally malformed. The goal is to simulate the unpredictable reality of production traffic.
Step 3: Feed Inputs into the System
The fuzzer sends these inputs to your application continuously. It tests how your system responds to data it was never trained or designed to handle.
Step 4: Monitor the Behavior
While the inputs are being tested, the system is watched closely. If there is a crash, memory leak, unexpected exception, or slowdown, the fuzzer flags it. This monitoring step is what turns random testing into valuable insights.
Step 5: Capture and Save Crashes
Every time the application behaves incorrectly, the fuzzer captures the exact input that caused the problem. This is important because it gives developers a reproducible test case. Without this step, debugging would be painful.
Step 6: Minimize the Failing Input
Many tools automatically reduce the failing test to the smallest possible input that still triggers the issue. This helps developers fix the root cause faster.
Step 7: Create Reports for Developers
Finally, the fuzzer generates a report that includes:
- The failing input
- The type of crash
- Logs and stack traces
- Coverage insights
This makes the issue clear and actionable for the development team.
Types of Fuzz Testing
Fuzz testing comes in several forms. Each is designed to uncover different kinds of weaknesses. The right approach depends on your product, architecture, compliance needs, and the level of security your business must maintain.
Below are the core types of fuzz testing used in modern engineering teams.
1. Black-Box Fuzzing
Black-box fuzzing treats your application like a sealed system. The tester has no visibility into the internal code. The fuzzer simply pushes random or malformed inputs and observes how the system reacts. This type of fuzz testing is a simple starting point for teams new to fuzz testing.
Best for:
- Quick and broad vulnerability discovery
- Applications with large, unpredictable input surfaces
- Teams that want early-stage security insights without deep instrumentation
2. Grey-Box or Coverage-Guided Fuzzing
Grey-box fuzzing uses instrumentation to monitor which parts of the code are being executed. The fuzzer learns from each test, continuously refining inputs to reach deeper logic paths. This is the most effective and popular fuzzing approach today because of its balance of automation, intelligence, and depth.
Best for:
- High-risk workflows
- Complex codebases with many hidden paths
- Vulnerability discovery in business-critical systems
3. White-Box Fuzzing
White-box fuzzers have full access to the source code. They analyze logic, data flows, and conditional paths and generate highly targeted inputs. This type of fuzz testing is deep and thorough, but expensive and resource heavy, which makes it ideal for businesses where failure is not an option.
Best for:
- Applications requiring strict compliance
- Systems with complex internal calculations
- Safety-critical workflows
4. API Fuzzing
API fuzzers generate malformed, boundary, or unpredictable requests to test REST, SOAP, GraphQL, gRPC, or internal service APIs. If your business depends on APIs, this is non-negotiable. API failures lead directly to downtime, data leaks, and broken customer workflows.
Best for:
- Microservice-based applications
- Platforms handling sensitive data through APIs
- High-traffic SaaS and mobile apps
5. Protocol Fuzzing
Protocol fuzzers attack communication channels like HTTP, TCP/IP, MQTT, CAN bus, or custom enterprise protocols. They manipulate handshake processes, packet structures, and message formats. This software testing is critical for any hardware-driven product or platform with real-time communication.
Best for:
- Systems reliant on device communication
- IoT ecosystems
- Automotive networks and control units
- Enterprise platforms built on custom protocols
6. File Format Fuzzing
File fuzzers alter or corrupt files to test how your application handles parsing, uploads, conversions, and processing. If users upload or download files, file fuzzing protects you from silent parsing vulnerabilities that often lead to the most serious security issues.
Best for:
- Products using files as core inputs (images, PDFs, spreadsheets, videos)
- Workflows that require user-generated content
- Systems vulnerable to file injection or parsing bugs
Which Fuzz Testing Types Does Your Business Actually Need?
This table shows industries that benefit most from each type of fuzz testing.
|
Industry |
Recommended Fuzz Testing Types |
|
Fintech |
Coverage-guided, API, white-box |
| Healthcare | White-box, file format, coverage-guided |
| SaaS | API, black-box, coverage-guided |
| IoT | Protocol, grey-box, file format |
| eCommerce | API, black-box, file format |
| Automotive |
Protocol, white-box, coverage-guided |
10 Best Fuzz Testing Tools
Most blogs throw random tool names at you. But if you’re running a business, you’re not looking for a list. You need clarity on which fuzz testing tools are actually worth using, what they do best, and how to choose one without wasting time or budget.
Below is a practical, enterprise-focused breakdown of today’s most reliable fuzzing tools and when to use them.
| Tool Category | Tool Name | Best Use Case / Strength |
| Coverage-Guided | AFL++ | Broad language support, good for memory bugs |
| libFuzzer | Unit-level fuzzing, integrates with sanitizers | |
| Honggfuzz | Easy to set up, good memory bug discovery | |
| Enterprise / Commercial | Peach Fuzzer | Protocol/file format fuzzing, strong automation |
| beSTORM | Deep protocol fuzzing, excellent for IoT & networking | |
| Synopsys Defensics | Large test library, compliance focus | |
| API Fuzzing | Burp Suite Extensions | API and security-centric testing |
| Schemathesis | Schema-driven API fuzzing (REST/GraphQL) | |
| Language Specific | Jazzer (Java) | JVM apps, Spring Boot, deep coverage |
| go-fuzz (Go) | Cloud-native Go apps, lightweight setup |
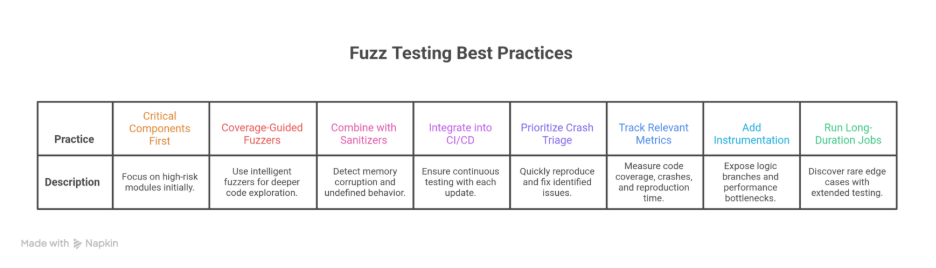
8 Best Practices for Effective Fuzz Testing
Fuzz testing delivers real value only when it is planned, structured, and integrated into your development workflow. Many teams run fuzzers for a few minutes, find nothing interesting, and assume their system is safe.
In reality, effective fuzzing requires strategy and consistency. Below are the most important fuzz testing best practices that enterprise teams should follow if they want meaningful coverage and real vulnerability discovery.
 1. Start with the Most Critical Components
1. Start with the Most Critical Components
Begin with modules that directly impact business risk: authentication flows, payment gateways, API gateways, file parsers, and anything tied to customer data.
It helps you discover high-severity issues early, reduces long-term exposure, and gives your security team more time to fix vulnerabilities before they compound across the codebase.
2. Use Coverage-Guided Fuzzers Instead of Pure Random Inputs
Random fuzzing is fast but shallow. Coverage-guided fuzzers like AFL++, libFuzzer, or Honggfuzz actually learn from each test case and move deeper into your code.
With this fuzz testing practice, you get higher code coverage and a greater chance of uncovering hidden logic bugs that traditional testing misses.
3. Combine Fuzzing With Sanitizers (ASAN, UBSAN, MSAN)
Sanitizers detect memory corruption, undefined behavior, and memory leaks while the fuzzer is running.
Most crashes become far easier to diagnose with Sanitizers as it turns subtle defects into clear failures before they become customer-facing issues.
4. Integrate Fuzzing Into CI/CD for Continuous Coverage
Running fuzzing only before release is risky. Security vulnerabilities accumulate quietly as the codebase grows.
CI-based fuzzing ensures every pull request and update is automatically tested. This fuzz testing approach reduces regression risks and catches new flaws early when they are cheaper to fix.
5. Prioritize Crash Triage and Quick Reproduction
A fuzzing job that finds crashes is only useful if your engineering team can reproduce and fix the issue quickly.
Fast triage reduces debugging time. Enterprises save engineering hours, shorten release cycles, and improve overall product stability.
6. Track Metrics That Actually Matter
Don’t measure success by the number of hours your fuzzer runs. Measuring the right metrics helps your security leaders understand improvement over time and justify investment in fuzzing infrastructure. Track:
- Code coverage
- Number of unique crashes
- Time to reproduce each crash
- Runtime performance
- Sanitizer errors
- Stability of the fuzzing environment
7. Add Security and Performance Instrumentation
Instrumentation tools help fuzzers explore deeper code paths by exposing logic branches and performance bottlenecks.
You get to detect vulnerabilities earlier and generate higher-quality test cases for future regression testing.
8. Run Long-Duration Fuzzing Jobs Overnight
Short fuzzing runs are ideal for quick checks. But the most serious bugs often appear during long-duration tests.
Overnight or weekend fuzzing sessions help discover rare edge cases and state transitions that fast or short fuzzers miss. This reduces long-term security risks at almost zero operational cost.
How to Integrate Fuzz Testing into CI/CD
Most enterprises want fuzz testing. But very few know how to integrate it into their DevSecOps pipeline without slowing development. The good news is that modern fuzzers can be automated, containerized, and monitored just like any other CI process.
Here is how enterprises should integrate it without slowing down releases.
1. Add Fuzzing at the RightDevSecOpsStages
In a mature DevSecOps system, fuzz testing sits right between:
Static checks (SAST) → Build → Fuzzing → Dynamic testing (DAST) → Release
This creates a consistent, automated safety net around your most critical code paths.
2. PlugFuzzersinto Your Existing CI Tools
Your CI system doesn’t need a big redesign. The common workflows look like this:
GitHub Actions
- Run fuzzers as separate jobs with dedicated runners.
- Auto-upload crash artifacts to GitHub Artifacts.
- Trigger fuzzing only on PRs touching critical components.
GitLab CI
- Use Docker-based fuzz jobs that spin up quickly.
- Add coverage thresholds in .gitlab-ci.yml.
- Integrate with GitLab’s built-in security dashboards.
Jenkins
- Configure pipeline stages that execute fuzz cases inside containers.
- Use Jenkins plugins for artifact retention and reporting.
- Parallelize fuzzing jobs for speed.
3. Automate Crash Detection and Reporting
- Manual crash hunting is not scalable. A solid CI/CD fuzzing setup should:
- Automatically flag crashes and hangs
- Store minimized test cases for fast reproduction
- Trigger issue creation in Jira or GitHub Issues
- Provide metadata like stack traces, sanitizer logs, coverage diffs
4. Use Containerization for Scalable Fuzz Testing
Container-based fuzzing makes it easier to run nightly or 24-hour fuzz rounds without tying up your main CI runners. Most QA experts run fuzzers inside Docker containers or Kubernetes jobs because:
- It ensures consistent environments
- It isolates fuzzers that may intentionally crash apps
- It scales fuzzing across multiple nodes
- It enables long, parallel fuzz runs without affecting CI performance
5. Combine FuzzingwithSAST and DAST
Fuzzing becomes exponentially more valuable when it is paired. Together, these tools provide a more complete security posture compared to traditional scanning alone.
- SAST for catching code-level issues
- DAST for finding runtime vulnerabilities
- IAST for deeper instrumentation during fuzzing runs
Where Fuzz Testing Delivers Real ROI for Businesses
Fuzz testing is one of the rare engineering investments that directly reduces outages and lowers long-term operational costs. When applied to the right components, it detects unpredictable failures that cause customer dissatisfaction.
1. Preventing Payment Failures Before They Hit Production
Payment systems are extremely sensitive to malformed or unexpected inputs. Fuzzing helps uncover issues like token parsing failures and signature validation bugs long before customers encounter them.
2. Catching Authentication and Token Validation Bugs
Fuzzing reveals vulnerabilities such as JWT misconfigurations and authorization bypass paths that normal testing misses. Fixing these early strengthens your security posture and reduces compliance risks.
3. Making APIs More Resilient to Unexpected Input
APIs fail not because of expected usage, but because real clients send corrupted JSON or unexpected enum values. Schema-driven API fuzzing exposes these weaknesses early and reduces production incidents across microservices.
4. Stopping Crashes in Customer-Critical Journeys
Signup flows and checkout pages are highly sensitive to input anomalies. Fuzzing detects hidden memory leaks that lead to app crashes or slowdowns. This directly improves retention and user satisfaction.
5. Boosting Reliability in IoT, Automotive, and Embedded Systems
Fuzzing helps identify failures in Bluetooth, MQTT, CAN, sensor inputs, and firmware updates. This strengthens compliance, safety, and long-term device reliability.
6. Strengthening Cloud Microservices That Talk to Unknown Clients
Modern cloud services interact with third-party systems and legacy clients. Fuzzing uncovers serialization errors and unhandled exceptions that can cascade into outages. The result is higher uptime and more stable distributed systems.
Fuzz Testing Challenges and Why Most Companies Need Expert Support
Fuzz testing delivers strong ROI. But it’s not simple to implement. Most engineering teams struggle because fuzzing requires deep tooling knowledge and continuous monitoring to deliver meaningful results. Below are the major challenges companies face and how our expert software development company removes them.
1. Hard to Configure Correctly
Fuzzers need accurate input models, dictionaries, coverage instrumentation, and isolated environments. A small misconfiguration can lead to low coverage or meaningless findings.
When you hire software testers from us, they handle full setup and configuration, build proper harnesses, prepare seed corpuses, and tune fuzzers to your tech stack so you get real, actionable results from day one.
2. High Computational Demand
Effective fuzzing requires long-duration runs and significant compute power. Many teams don’t have the infrastructure or budget planning for this.
Our team run and manage long-duration fuzz jobs using optimized resource allocation, container orchestration, and scalable infrastructure so your team never has to worry about compute overhead.
3. Need for Crash Triage Expertise
Fuzzers produce hundreds of crashes and only a few are truly important. Without deep triage skills, teams waste hours on duplicates or low-severity issues.
Our software testing company analyze, de-duplicate, and prioritize crashes by severity. You only receive verified, reproducible bugs with clear impact and recommended fixes.
4. Tool Selection Complexity
Choosing between AFL++, libFuzzer, Honggfuzz, Peach, Defensics, or API-specific tools requires experience. Using the wrong tool leads to poor results and wasted effort.
We select and configure the right fuzzing tools based on your architecture, language, compliance needs, and business goals to ensure maximum coverage and efficiency.
5. Difficulty Reproducing Failures
Fuzz-generated failures can be unstable and hard to replicate. Without proper instrumentation, debugging becomes slow and painful.
Our automation testing company configures instrumentation, sanitizers, logging, and environment isolation to ensure every crash is fully reproducible with step-by-step traces and exact payloads.
6. Time-Consuming Maintenance
Fuzz testing requires continuous updates, new inputs, regenerated corpuses, and integration with changing codebases.
We maintain your fuzzing workflows end-to-end, update corpuses, monitor runs, integrate with CI/CD pipeline, and provide regular reports so fuzz testing stays effective as your product evolves.
Conclusion
Fuzz testing is no longer an experimental technique reserved for security labs. It has become a practical way for enterprises to harden their products, protect customer data, and avoid expensive incidents.
When done right, it strengthens your security posture, builds long-term customer trust, and prevents issues that could easily turn into outages or PR problems. It also saves teams time and money by catching unpredictable failures early instead of fighting fires late in the release cycle.
FAQs
Q1. Is fuzz testing expensive?
Ans. Fuzz testing is affordable compared to the cost of downtime, security breaches, or customer facing failures. Most businesses start small with targeted fuzzing and scale based on product complexity.
Q2. Does fuzz testing replace penetration testing?
Ans. No. Fuzz testing complements penetration testing. Fuzzers uncover unexpected crashes and edge cases, while penetration tests evaluate real attack scenarios. Together they give stronger coverage.
Q3. How long does fuzz testing take?
Ans. Initial setup can take a few days. After that, fuzzing runs continuously in the background and starts surfacing issues within hours. Mature programs integrate fuzzers directly into CI/CD for ongoing coverage.
Q4. Do startups need fuzz testing?
Ans. Yes, especially if the product handles payments, authentication, APIs, or user uploaded content. Startups benefit from early detection because fixing issues later becomes far more expensive.
Q5. Is fuzz testing only for security testing?
Ans. No. Fuzzing also improves reliability, performance, and stability. It catches crashes, memory issues, and logic errors that functional testing and automation usually miss.
Q6. Can fuzzing slow down CI/CD pipelines?
Ans. Not if configured correctly. Fuzz testing typically runs in parallel to CI pipelines, with targeted runs for critical components. It provides fast feedback without slowing releases.
Q7. How do enterprises choose the right fuzz testing tool?
Ans. Enterprises compare tools based on input model support, automation level, crash triage features, integration with CI, and scalability. Most companies prefer expert guidance because tool selection directly affects coverage and ROI.


 1. Start with the Most Critical Components
1. Start with the Most Critical Components



