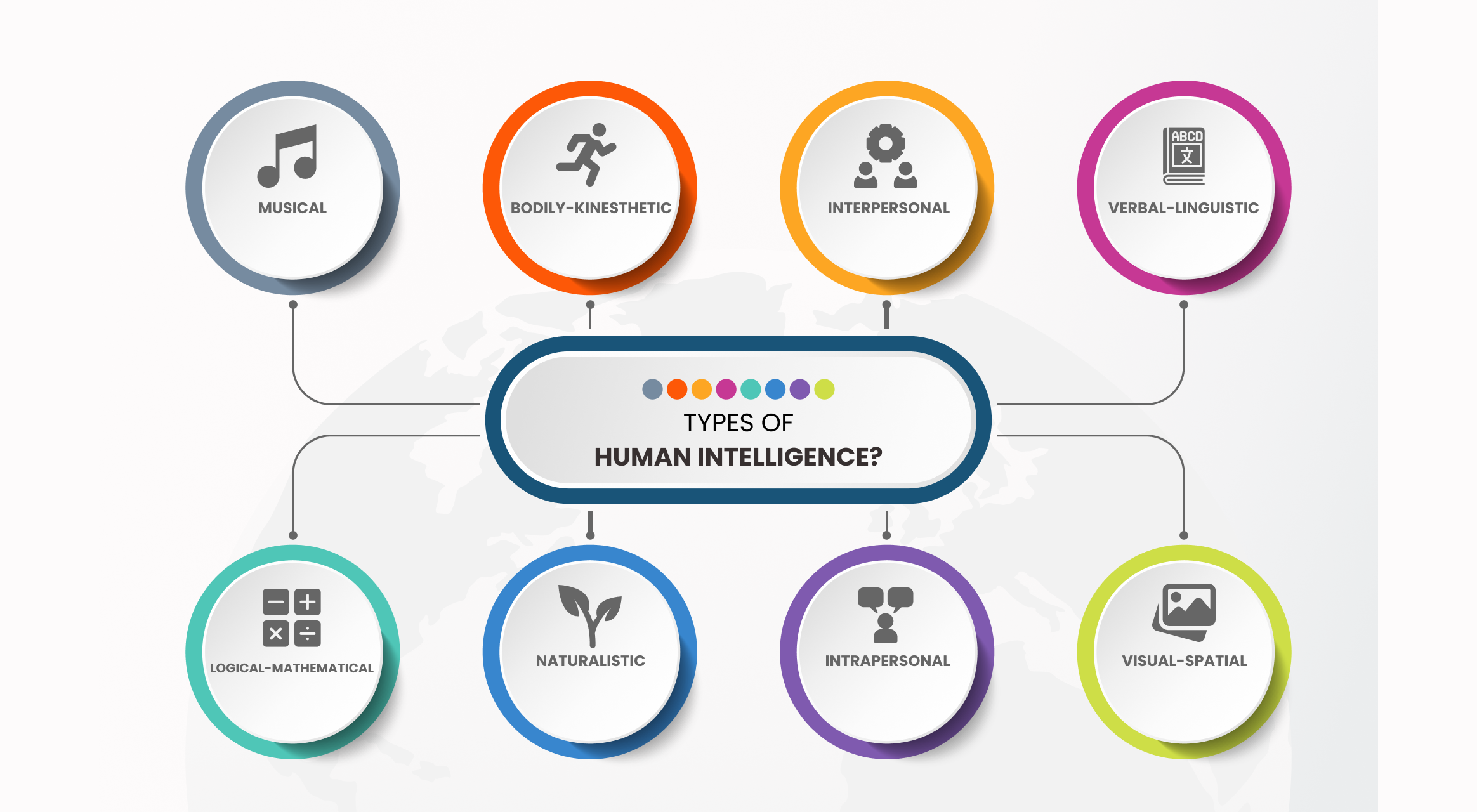
Here’s what you will learn:
When discussing Artificial Intelligence (AI) in comparison to Human Intelligence, a compelling contrast emerges. This comparison, often framed as AI Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence, delves into the intricacies of language and thought processes. AI exhibits the capability to utilize concise, straightforward terminology as well as extended, intricate sentence structures, mirroring the versatility of skilled human writers. This exploration of the difference between Human Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence underscores the captivating nuances within the AI field.
For those captivated by the differentiation between Human Intelligence and AI or those embarking on the path of AI solutions like Conversational AI solutions, Generative AI, Machine Learning solutions, and NLP solutions, an exciting voyage awaits, full of exploration and enchantment.
So, Lets dive into the discussion of Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence.
Table of Contents
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, often referred to as AI, is a subfield of computer science focused on imbuing machines with human-like intelligence. This involves enabling machines to comprehend language, make decisions, and even operate vehicles, tasks typically associated with human cognition. AI relies on mathematical principles and learning algorithms to simulate human thought processes within computer systems.
The complexity of AI becomes evident when it grapples with human language. It can communicate in short, precise sentences or craft extended, detailed narratives akin to a skilled writer. This inherent diversity in its communication style makes AI an intriguing and often unpredictable entity. To truly grasp AI, one must appreciate its ability to navigate the fine line between complexity and adaptability when conveying ideas in human language.
Read Also – How Generative AI is Reshaping the Automotive Industry (2023)
What is Human Intelligence?
Human intelligence, often contrasted with artificial human intelligence, encompasses an inherent capacity within individuals for learning, cognition, reasoning, adaptation, and problem-solving. This diverse cognitive ability involves functions like memory, perception, language, and emotional comprehension. It forms the basis for efficient information processing, decision-making, experiential learning, and critical thinking, derived from a combination of distinct mental faculties rather than a singular skill.
Human intelligence empowers effective communication, artistic expression, technological progress, and a profound comprehension of the surrounding world. It is marked by its adaptability, creativity, and the ability to derive insights from both successes and failures. This foundational aspect defines the exceptional aptitude of humans in navigating the intricate intricacies of life and the universe.
Difference between Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence are two distinct forms of cognitive capabilities, each with its own strengths and limitations. Here’s a comparison between the two:
Learning Process:
- AI: AI learns through data and algorithms. It requires large amounts of data and training to acquire knowledge and improve performance.
- Human Intelligence: Humans learn through a combination of education, experience, and exposure. We can generalize knowledge from one domain to another and learn from fewer examples.
Processing Speed:
- AI: AI processes information at incredible speed, making it ideal for repetitive, high-speed tasks and computations.
- Human Intelligence: Human thinking is comparatively slower but more flexible and adaptable, excelling in tasks that require creativity, emotional understanding, and complex decision-making.
Creativity:
- AI: AI lacks true creativity. It can generate content based on patterns in data but doesn’t possess genuine creativity or imagination.
- Human Intelligence: Humans are inherently creative, capable of producing original ideas, art, music, and novel solutions to problems.
Emotional Intelligence:
- AI: AI has no emotional understanding or empathy. It doesn’t experience emotions or comprehend human emotional states without external input.
- Human Intelligence: Humans possess emotional intelligence, allowing us to understand and empathize with others, interpret non-verbal cues, and form social connections.
Adaptability:
- AI: AI is highly specialized and struggles to adapt to new, unforeseen situations without reprogramming or extensive training.
- Human Intelligence: Humans are remarkably adaptable, able to apply knowledge and skills across diverse situations and learn rapidly from novel experiences.
Error Handling:
- AI: AI is precise and consistent but can make errors when faced with unexpected or ambiguous situations.
- Human Intelligence: Humans are resilient in handling unexpected situations and uncertainties, but we are also prone to cognitive biases and errors.
Understanding Context:
- AI: AI can struggle with understanding the context and subtleties in language, humor, and sarcasm.
- Human Intelligence: Humans excel at grasping the nuances of context, idiomatic expressions, and the emotional tone in communication.
Biological vs. Synthetic:
- AI: AI is a product of human engineering and is made of computer code and data. It is synthetic and lacks consciousness.
- Human Intelligence: Human intelligence is biological and tied to the brain, involving consciousness, self-awareness, and subjective experience.
Read Also – AI in Manufacturing Industry
Will AI replace humans?
The ongoing debate revolves around whether artificial intelligence solutions will supplant humans. AI has demonstrated exceptional proficiency in task automation and efficiency enhancement. However, it lags in replicating distinct human attributes such as empathy, creativity, and intricate problem-solving. Although AI excels in specific domains, it grapples with navigating human emotions and ethical dilemmas, raising doubts about its potential to entirely replace humans in roles demanding these qualities.
In the shifting landscape of work and technology, it is essential to acknowledge that the Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence relationship is more likely to be synergistic rather than adversarial. AI can certainly assume certain job functions, but it also introduces fresh opportunities for humans to explore more creative and intellectually demanding roles. Instead of substitution, the future is expected to witness a dynamic partnership between AI and humans, with each complementing the strengths of the other, resulting in a more effective and innovative world.
Will AI change the Job Landscape?
The influence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on the employment landscape is a multifaceted and intricate matter, prompting us to ponder: “Will AI ultimately result in job displacement or job generation?” The response is nuanced and reliant on a multitude of variables, but one thing is evident – the coexistence of both job displacement and job creation will be a reality.
-
Job Displacement
AI and automation technologies have the potential to displace certain job roles, particularly those that involve repetitive and routine tasks. Jobs in manufacturing, customer service, data entry, and simple analysis are susceptible to automation. This displacement is already happening in some industries, leading to workforce changes. The fear of AI-driven job loss has been a prevalent concern.
-
Job Transformation
While AI can displace jobs, it also plays a significant role in transforming job roles and tasks. Many jobs will evolve as AI automates repetitive tasks, allowing workers to focus on more complex, creative, and strategic aspects of their work. For instance, in healthcare, AI can assist with diagnostic tasks, freeing up doctors to concentrate on patient care and complex medical decisions. This transformation can lead to increased job satisfaction and personal growth for employees.
-
Job Creation
The expansion of AI technology and its incorporation into diverse sectors is fostering fresh employment prospects. Professions associated with AI, like AI engineers, data scientists, machine learning specialists, and AI ethicists, are witnessing significant demand. These positions encompass the tasks of crafting, upholding, and guaranteeing the ethical deployment of AI systems. Furthermore, fields intricately linked with AI, such as robotics, self-driving vehicles, and data analysis, are spawning novel employment opportunities.
-
Skill Adaptation and Reskilling
The successful coexistence of humans and AI in the workforce depends on individuals’ ability to adapt and acquire new skills. Many existing job roles will require a mix of technical and soft skills to collaborate effectively with AI systems. This has led to a growing emphasis on continuous learning and reskilling. Employees and employers must invest in training and education to ensure that workers can thrive in an AI-augmented environment.
-
Sector-Specific Impacts
The effect of AI on jobs varies by industry. In some sectors, AI may have a more significant impact on job displacement, while in others, it drives more job creation. For example, AI in healthcare can lead to new roles in medical data analysis and telemedicine, whereas in the manufacturing industry, it might lead to the automation of certain manual tasks.
-
Global Workforce Dynamics
AI’s influence on the job market transcends national boundaries. It can lead to changes in the global workforce landscape as companies and industries worldwide adopt AI technologies. This shift can affect the outsourcing of tasks and jobs to other countries, as businesses seek to harness AI’s advantages while also considering regional skill availability and economic factors. The evolving global job market dynamics will require adaptability from both employees and businesses to remain competitive and effective on an international scale.
Read Also – Everything You Must Know About ChatGPT in 2023
How is AI transforming healthcare?
1- Diagnostic Assistance:
- Medical Image Analysis: AI analyzes medical images like X-rays and MRIs, helping identify anomalies and conditions more accurately and swiftly.
- Pathology and Histopathology Automation: It can also assist in pathology and histopathology by automating the analysis of tissue samples, improving accuracy and speed of diagnoses.
2- Treatment Recommendations:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: AI can suggest personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique medical history by analyzing vast patient data and clinical guidelines.
- Real-Time Treatment Adjustment: It can also monitor a patient’s response to treatment and adjust recommendations in real-time, ensuring more adaptive and effective care strategies.
3- Drug Discovery:
- Drug Interaction Simulation: AI accelerates drug discovery by simulating drug interactions and predicting their effectiveness.
- Clinical Trial Streamlining: It also streamlines the clinical trial process by identifying suitable candidates and helping researchers design more targeted experiments, saving both time and resources.
4- Predictive Analytics:
- Disease Outbreak Prediction: AI models can predict disease outbreaks, patient readmissions, and health risks by analyzing relevant data.
- Hospital Logistics Optimization: They also help in the optimization of hospital logistics and patient flow, ensuring efficient utilization of staff and equipment, thereby reducing wait times and improving patient satisfaction.
5- Telemedicine:
- Remote Patient-Professional Connection: AI-driven telemedicine solutions connect patients and healthcare professionals remotely, providing convenient and timely access to medical care.
- Chronic Condition Monitoring: They can also enhance remote monitoring of chronic conditions, enabling early intervention and reducing the burden on in-person healthcare services.
6- Patient Data Security:
- Data Encryption: Implement strong data encryption protocols to safeguard patient information, ensuring that it remains confidential and protected from potential threats.
- Access Control: Employ strict access controls and authentication measures to restrict data access only to authorized healthcare professionals, enhancing the security of patient records.
Read Also – How Generative AI Boosts Enterprise Growth in 2023?
How does AI impact Education?
1- Personalized Learning:
- Learning Pattern Analysis: AI algorithms analyze students’ learning patterns, identifying their strengths and weaknesses. This data enables AI to tailor educational content to each student’s pace and comprehension, ensuring a more effective and engaging learning experience.
- Real-Time Feedback and Resources: AI systems provide immediate feedback, highlighting areas where students need improvement. Additionally, they offer supplementary resources, exercises, and materials to address specific learning needs, promoting better understanding and retention.
2- Efficient Administrative Tasks:
- Automated Enrollment and Scheduling: AI streamlines administrative tasks by automating enrollment processes and creating optimized class schedules. This not only ensures that resources are allocated efficiently but also places students in suitable classes, improving overall educational organization.
- AI-Driven Grading Tools: AI-driven grading tools quickly and accurately assess assignments, quizzes, and exams. By automating the grading process, teachers save valuable time, allowing them to concentrate on more impactful aspects of instruction.
3- Enhanced Classroom Teaching:
- Interactive Smart Boards: AI-enabled smart boards empower teachers to craft interactive and dynamic lessons. With multimedia elements and interactive features, these tools encourage student participation and facilitate more engaging and effective learning experiences.
- AI-Powered Virtual Tutors: AI-driven virtual tutors extend support to students outside of regular class hours. They assist with homework, offer practice exercises, and respond to students’ questions, creating a more inclusive and effective learning environment.
4- Assessment and Feedback:
- Instant Grading and Feedback: AI accelerates the grading process by providing instant feedback on assignments and tests. This immediate feedback allows students to learn from their mistakes promptly, promoting continuous improvement.
- Data-Driven Student Support: AI analyzes student data to pinpoint areas where students may be struggling. These insights enable teachers to adapt their instruction to provide targeted support to individual students, fostering better learning outcomes.
5- Accessibility and Inclusivity:
- Real-Time Language Translation: AI offers real-time language translation services, breaking down language barriers and making educational content accessible to students who speak different languages. This fosters inclusivity and embraces cultural diversity.
- Captioning and Voice Recognition Technologies: AI-driven captioning and voice recognition technologies ensure that students with disabilities can actively participate and access educational content. This approach guarantees that learning materials are inclusive and accessible to all, regardless of physical or linguistic differences.
5- Personalized Study Plans:
- Progress Tracking: AI can continuously monitor a student’s progress in real-time, adjusting the study plan as needed based on their performance and learning speed.
- Resource Recommendations: AI can recommend a variety of learning resources such as textbooks, online courses, and educational apps tailored to the student’s specific learning needs and goals.
Are there any ethical concerns related to the future of AI that need to be addressed?
-
Bias and Fairness:
Bias in AI: AI algorithms learn from data, and if the training data is biased, the AI system can perpetuate that bias. For example, if historical hiring data favors certain demographics, an AI hiring system might unfairly discriminate against others.
Fairness: Ensuring fairness in AI systems means mitigating these biases. It involves developing algorithms and datasets that are representative and free from discriminatory patterns. Ethical AI development includes proactive measures to identify and rectify bias, ensuring that AI systems treat all individuals fairly and equitably.
-
Transparency and Accountability:
Transparency: AI decision-making can be complex and opaque, making it challenging for individuals to understand why a particular decision was made. This lack of transparency raises concerns about accountability. Transparency initiatives aim to make AI decision processes more understandable to users and regulators.
Accountability: Accountability involves identifying who is responsible for AI-driven decisions. It’s crucial to establish clear lines of responsibility when AI systems make significant decisions, particularly in situations where AI autonomously operates.
-
Privacy and Data Security:
Data Privacy: AI often relies on vast amounts of personal data, including sensitive information. Privacy concerns arise when this data is mishandled or misused. Individuals expect their data to be protected and used responsibly by AI systems.
Data Security: Ensuring the security of data is a critical ethical responsibility. Data breaches, leaks, or unauthorized access can have severe consequences. Ethical AI development includes robust data security measures to protect individuals’ information.
-
Job Displacement and Economic Impact:
Job Displacement: Automation and AI can lead to the displacement of certain job roles, which can be a source of economic and social disruption. Identifying roles at risk of automation and developing strategies for reskilling and transition is essential.
Economic Impact: Economic inequalities can be exacerbated if the benefits of AI are not equitably distributed. Ethical considerations require governments, organizations, and institutions to prioritize policies and programs that address these disparities, supporting affected workers and communities.
-
Security and Misuse:
Security Concerns: The increasing power and autonomy of AI technologies raise security concerns. Autonomous weapons and cyberattacks using AI can pose significant threats to national security and international stability.
Misuse: AI misuse, particularly in the development of autonomous weapons or deepfake technologies, is a grave ethical concern. It underscores the importance of international agreements, regulations, and responsible AI practices to prevent AI from causing harm or undermining security.
-
Algorithmic Accountability:
Responsibility of Developers: AI systems should come with clearly defined lines of responsibility, outlining who is accountable for the decisions made by the Ai Developers and organizations should take ownership of their AI systems’ actions.
Protocols and Mechanisms: Establishing clear protocols and mechanisms is essential to assess and address errors, biases, and unintended outcomes in AI systems. This ensures transparency and accountability in AI development and usage.
What are the Key Takeaways of Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence?
In conclusion, the comparison between artificial intelligence vs human intelligence highlights that both possess unique strengths and limitations. AI is excellent at handling tasks that need speed, efficiency, and recognizing patterns. Meanwhile, human intelligence stands out in areas that demand creativity, understanding emotions, and making ethical judgments. It excels in tasks requiring rapid data processing and automation, while human intelligence offers emotional understanding, creativity, and moral judgment that AI cannot replicate. Rather than pitting them against each other, the future promises a harmonious fusion of AI and human intelligence, unlocking their combined potential to enhance various aspects of our lives. It’s not a question of one prevailing over the other, but the collaborative interaction between both that holds the key to a brighter future.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes AI from human intelligence at its core?
AI primarily operates using algorithms, data, and computational capabilities for task execution. In contrast, human intelligence encompasses intricate cognitive processes, emotional understanding, and the flexibility to adapt to diverse situations.
2. Can AI replace humans in all job roles?
While AI can automate many tasks, it struggles with roles requiring creativity, empathy, and nuanced decision-making. The future is likely to see a partnership between AI and humans, where they complement each other.
3. What are the ethical concerns associated with AI development and deployment?
Ethical concerns include bias in AI algorithms, transparency and accountability in AI decision-making, privacy and data security, job displacement, and security issues, such as AI misuse and autonomous weapons.
4. How does AI impact healthcare, and what are its benefits?
AI enhances healthcare by assisting in diagnostics, suggesting personalized treatment plans, streamlining drug discovery, and offering predictive analytics. These applications lead to faster and more accurate medical services.
5. In the field of education, how does AI contribute to personalized learning?
AI personalizes education by analyzing students’ learning patterns, providing real-time feedback, automating administrative tasks, enhancing classroom teaching, and offering personalized study plans. This approach fosters more effective and inclusive learning experiences.