
Here’s what you will learn:
Cybersecurity has never been easy. And today, it’s getting even harder.
Attackers are using AI to find vulnerabilities faster, dodge detection, and launch attacks we’ve never seen before. But here’s the good news: we can fight fire with fire.
AI is becoming one of the most powerful tools we have to detect, prevent, and respond to these new-age threats. In this article, we’ll break down (in simple language) how AI is reshaping cybersecurity, what tools are worth paying attention to, and how you can actually use AI instead of just throwing buzzwords around.
Let’s get into it.
Table of Contents
Why is AI for cybersecurity important?
First, some real talk: – even with AI investments, almost half of companies (47%) still faced more than 10 breaches last year, according to Cloudflare.
And 87% believe AI has made cyberattacks even more sophisticated. Crazy, right?
Attackers aren’t just sitting back but are using AI to automate attacks, crack passwords, mimic humans, and even outsmart basic security tools.
But if they can use AI to get smarter, so can we.
That’s why AI isn’t just a “nice to have” anymore. It’s becoming a core part of cybersecurity services.
AI and Cybersecurity: Then and Now

Artificial Intelligence has been changing the enterprise world for decades. But keeping systems secure isn’t just the job of security teams anymore.
In the past, security was pretty basic. Back in the 1980s, companies relied on rule-based systems. Think of it like setting up a security alarm that only goes off under very specific conditions. It worked until attackers found ways around it.
Fast forward to the 2000s, and machine learning entered the picture. Suddenly, security systems could “learn” from patterns. They weren’t just reacting anymore. They could spot odd behavior in huge amounts of network traffic, even when no clear rules existed.
Today, AI in cybersecurity has become even smarter. It doesn’t just detect threats. But it can predict them, organize complex data, and even understand natural human language. This means security teams can ask AI simple questions, get faster insights, and take action before an attack becomes a crisis.
But with great power comes new risks. Now, even everyday users need to think twice before sharing sensitive information with AI tools, as leaks and exposure are very real threats.
The journey from basic alarms to intelligent defenses shows just how deeply AI has woven itself into cybersecurity and it’s only just getting started.
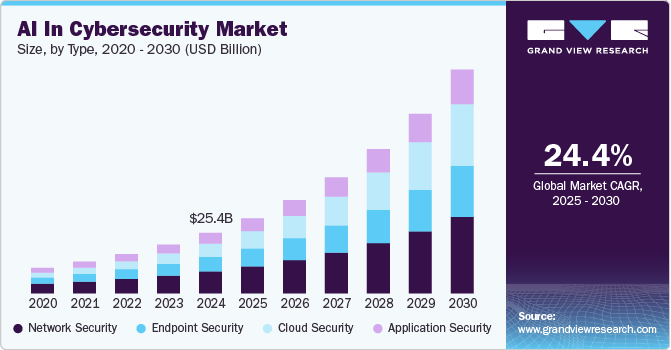
Image taken from GrandViewResearch
Role of AI in Cyber Security
Not every shiny AI product is useful. But here are some common uses of security practices integrated with AI to help professionals.
Identity and access management
AI helps analyze past user behavior and sign-in patterns. This makes it easier to detect unusual login activity or possible threats.
If you hire cybersecurity engineers who have expertise in AI, they can get a deeper view of potential risks both on the surface and hidden.
AI can work with two-factor authentication (2FA) systems to add another layer of security. Only users who pass these checks can gain access.
Endpoint security and management
AI helps security professionals identify and monitor all endpoints across a network. It also ensures that devices are running the latest operating system updates.
In addition, AI-powered tools can detect signs of potential malware before it causes harm.
Cloud Security
The use of Artificial Intelligence in cloud security is crucial. As this combination of AI plus cybersecurity helps to manage the infrastructure of the cloud providers from various vendors. You can hire AI developers alongside your cybersecurity team to gain visibility across the multi-cloud risks.
Information protection
AI helps security teams find sensitive data in the digital world. It also protects cloud-based applications used by businesses.
With AI, you can detect outsiders trying to access or damage your confidential data and quickly block them before harm is done.
Incident investigation and response
Lastly the incident response. AI helps security teams quickly spot and respond to potential threats. It can gather and connect data from different sources to find patterns.
AI also uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to language-based queries. This makes it easier for professionals to investigate issues and get quick answers.
Advantages of deploying AI in cybersecurity
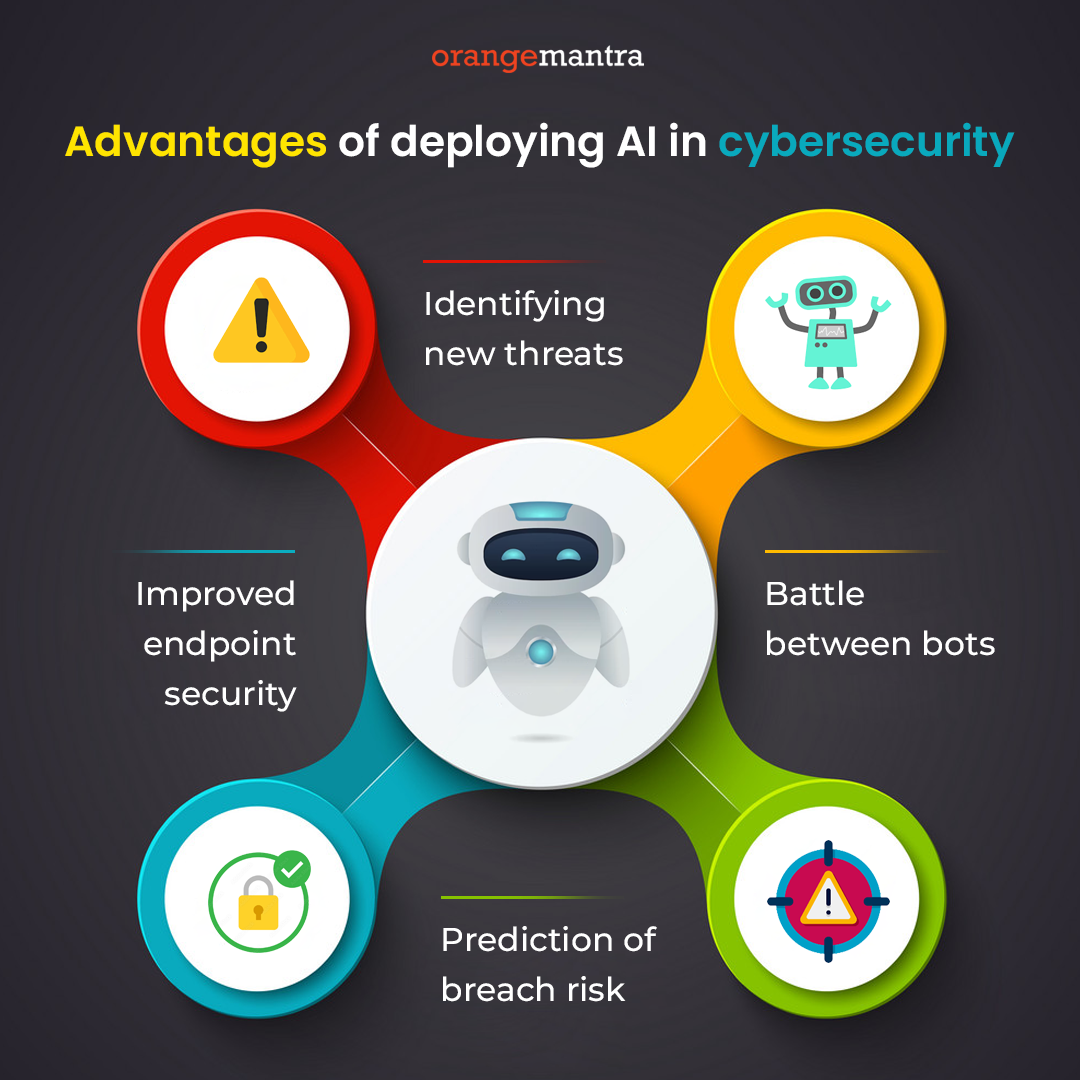
As AI has demonstrated numerous benefits to various industries, here are some edges it can provide to cybersecurity.
Identifying new threats
AI agent detects cyber threats and suspicious behavior that traditional tools lack. It spots malware early using smart algorithms, even detecting small signs before an attack happens. AI also identifies new threats and suggests prevention strategies.
Battle between bots
Bots account for a significant portion of internet traffic today and can be dangerous. Bots can be a real threat, from account takeovers using stolen credentials to bogus account creation and data fraud.
Manual responses will not suffice to combat automated threats. AI and machine learning assist in developing a comprehensive understanding of website between good bots and bad bots.
AI allows us to analyze massive amounts of data and helps cybersecurity expert teams strategize in an ever-changing landscape. You can consider conversational AI solutions to configure bots according to your niche.
Prediction of breach risk
Cybersecurity AI systems assists in determining the IT asset inventory, which is a detailed record of all devices with varying levels of access to various devices. AI-based frameworks can predict how and where you are most likely to be compromised, allowing you to plan and allocate resources to the most vulnerable areas.
The AI-based analysis provides predictive insights that allow you to configure and improve controls and processes to strengthen your cyber resilience.
Improved endpoint security
The number of devices used for remote work is rapidly increasing. AI for cybersecurity will play a critical role in securing all endpoints. Moreover, antivirus software and VPNs can help protect against remote malware and ransomware attacks, but they frequently rely on signatures.
AI in cybersecurity stays ahead of new threats without needing regular signature updates. If antivirus software isn’t updated or the vendor misses a new threat, signature-based protection may fail. This is where AI’s ability to detect new types of malwares becomes crucial.
Also read: Cyber Security vs Information Security
Top AI Based Cybersecurity Tools
Integration of AI security tools into cybersecurity improves effectiveness. Here are some to look at as per our AI development company:
| Tool | What It Does |
| Darktrace | Detects threats across network, cloud, IoT, and email using self-learning AI. |
| CrowdStrike Falcon | AI-powered endpoint protection, EDR, and threat hunting. |
| CylancePROTECT (Blackberry) | Predicts and blocks malware with AI before it executes. |
| Microsoft Defender for Endpoint | Cloud-based AI defense for endpoints across platforms. |
| Vectra AI | Detects hidden threats in hybrid and multi-cloud environments. |
| SentinelOne Singularity Platform | Autonomous AI-driven endpoint protection and XDR. |
| IBM Security QRadar Suite | AI-driven SIEM and SOAR platform for threat detection and response. |
| Cortex XDR (Palo Alto Networks) | Extended Detection and Response platform with AI analytics. |
| Tessian | Secures human-layer threats like phishing, insider risks, and misdirected emails. |
| LogRhythm Axon | Cloud-native SIEM platform with AI-based threat detection. |
8 Best Practices to Employ AI in Cybersecurity
It sounds very exciting when we say we are going to use AI in cybersecurity. But to make it truly work for your organization, it needs to be done thoughtfully.
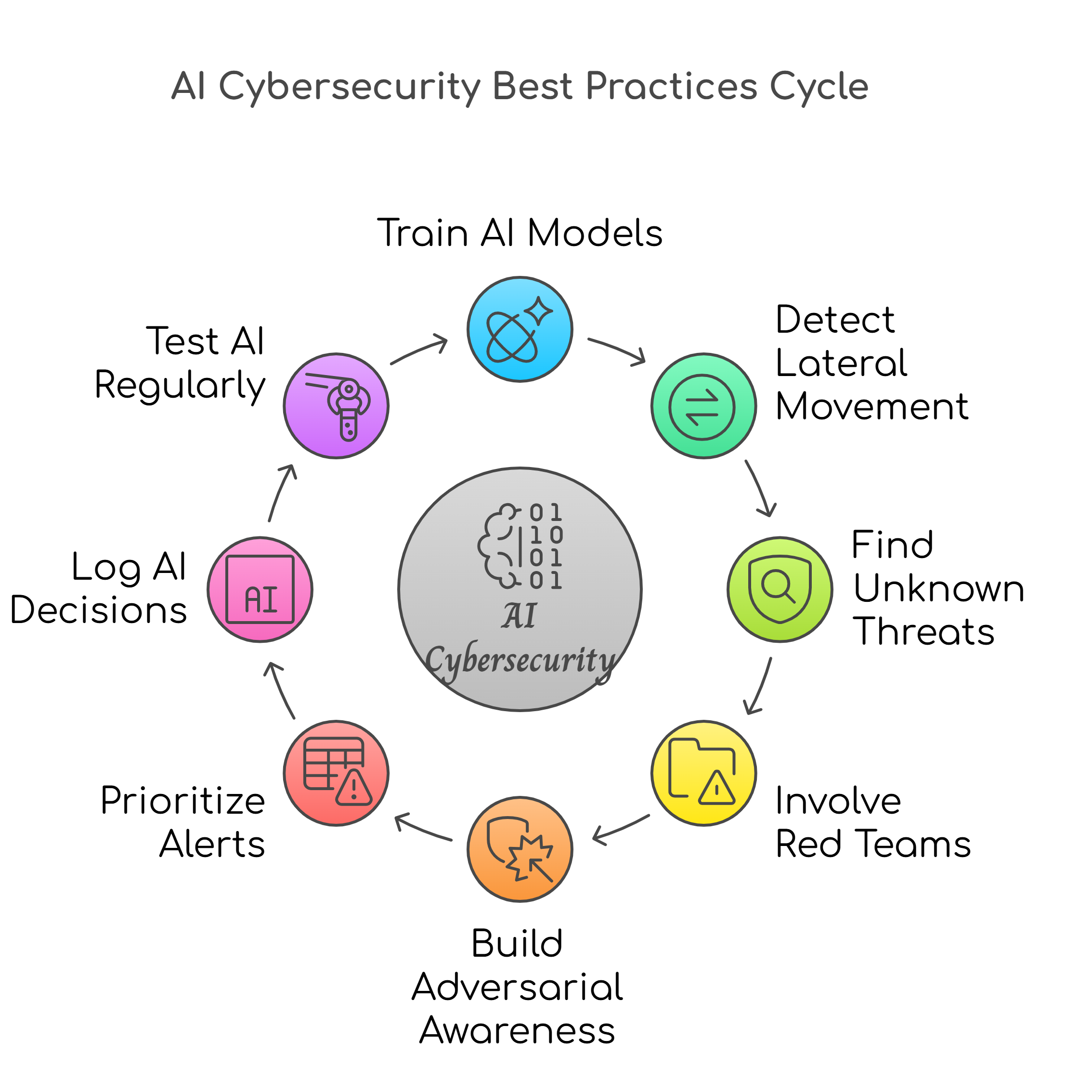
Here are some of the key practices that can help businesses get the most out of AI-powered security tools.
Train AI models on your internal threat DNA
Most companies rely on off-the-shelf AI models trained on global threat feeds. While useful, these models don’t understand your unique environment like your network behavior, internal tools, or known “safe” anomalies.
So, build a feedback loop between your SIEM and AI platform using real security incidents from your environment. Train your models to recognize your company’s normal vs risky behavior.
This helps reduce alert fatigue by cutting down false positives that are “technically suspicious” but safe in your context.
Use AI for lateral movement detection
Many organizations still use AI only at the entry points (e.g., emails, endpoints). But modern attackers don’t stop at the door. Once inside, they move laterally, blend in, and escalate privileges quietly.
As expert, we advise you to deploy AI across internal network traffic between systems. Train it to detect small deviations in lateral activity, such as:
- Unusual service account activity
- Resource access from odd locations or times
- Abnormal SMB or RDP connections
AI can stitch together weak signals across time and space to detect hidden movements that traditional tools miss.
Use unsupervised learning to find “unknown unknowns”
Most AI tools for cybersecurity rely on supervised learning. They detect threats they’ve seen before. But the real advantage of AI is in spotting novel behaviors like anomalies no human has labeled as dangerous yet.
An expert approach should be to pair supervised learning (for known threats) with unsupervised learning models that cluster user or device behavior and flag patterns that don’t fit.
Involve red teams in model training
Want smarter AI? Feed it better attacks.
Invite your red team or ethical hackers to perform internal attack simulations and let your AI models learn from those behaviors. This is more realistic than lab data and exposes the AI to real adversarial thinking; lateral movement, credential theft, insider threat patterns, etc.
Some mature orgs even run “AI vs red team” scenarios to see how their AI agent evolves in response to new tactics.
Build adversarial awareness into your models
Yes, attackers are now using AI to bypass AI. Think adversarial attacks: slightly modified malware that fools models into thinking it’s safe. Or poisoned data injected into your logs to corrupt learning.
How to respond:
- Regularly test your models with adversarial examples (slightly obfuscated threats) to see what slips through.
- Apply adversarial training: retrain your models on tricked samples so they become more resilient.
- Limit external input sources the AI learns from; to reduce poisoning risks.
Use AI to prioritize alerts based on business impact, not just threat level
AI can classify severity. But what’s severe in general may be low risk in your business context. For example, a brute-force attack on a low-privilege test account may not matter as much as suspicious access to a revenue-critical database.
Integrate your AI system with asset management and business priority tags. Let it weigh alerts not just on how “bad” they are, but how much damage they could do to your core services. This is how smart SOCs cut through the noise and triage faster.
Log AI decisions for compliance and audit-readiness
AI decisions aren’t just for alerts, but they often trigger automated actions. If a model isolates a device, kills a process, or restricts access, you need a paper trail. This is very important for:
- Regulatory audits (e.g., SOX, PCI-DSS, HIPAA)
- Explaining why a system was taken down
- Defending actions during post-incident reviews
We advise you to use an AI system with built-in explainability and audit logging. It should show not only what decision was made, but why, based on which signals, and when.
Test your AI like you test your backups
Don’t assume it works. Pro teams treat AI like any other critical security component; they test it regularly.
How?
Below given stress tests reveal blind spots and help you tune in to real-world messiness.
- Inject synthetic threats into the environment and see if AI catches them.
- Create scenarios where multiple weak signals need to be correlated; does the AI connect the dots?
- Turn off a data source (like DNS logs) and test how the AI handles incomplete data.
Also read: How to select reliable cybersecurity services?
The future of AI for cybersecurity

As we have understood how AI can transform the industry with its incredible benefits. So, now we jump to its potential future. The role of AI will grow significantly growth for security professionals.
- The AI for cybersecurity will improve to detection of cyber threats with fewer positive points.
- Security operations teams automate complex processes to respond to AI cyber-attacks.
- Enterprises will use AI to integrate and address vulnerabilities to improve the security process.
- The security teams will increase the high demand.
- Users help to take up strategic roles to proactively hunt down cyber threats.
The Flip Side: Cybercriminals Using AI Too
It’s important to remember, AI isn’t just a tool for defenders. Cybercriminals are investing heavily in AI to boost their own attacks.
Here’s how they might use it:
- AI can quickly analyze huge data leaks to find valuable targets like financial records or login credentials.
- AI can personalize phishing emails to make them look incredibly convincing.
- Attackers can create malware that adapts its behavior to avoid traditional detection methods.
Also check: How to incorporate Cybersecurity in IoT for businesses?
Conclusion
The future of AI in cybersecurity is bright. But let’s accept it is not without challenges. AI is going to be our war buddy in the fight against cybercrime. It’s helping businesses, governments, and individuals stay one step ahead of ever-evolving threats.
Like any powerful technology, AI must be used responsibly. The idea should be to protect, not to harm.
The ability of AI to predict, detect, and respond to threats in real time will continue to make it an invaluable asset. If you want to make AI work for your cybersecurity, you can contact us.
FAQs
-
What is the role of AI in cybersecurity?
AI take cybersecurity to the next level by detecting, predicting, and responding to cyber threats faster and more accurately. AI gives us the power to analyze buckets of data to identify potential vulnerabilities, unusual behavior, and malicious activities. AI security tools also automate tasks, reduce false positives, and strengthen defenses against new age cyberattacks.
-
How does AI stop hackers?
AI is the most advanced tech in human history, and it is used by both attackers and defenders. We can use AI to stop hackers. How? Well, by continuously monitoring networks for abnormal activities and identifying threats before they cause harm. AI can also automatically block suspicious activities and respond to threats in real-time.
-
What is responsible AI in cybersecurity?
Responsible AI in cybersecurity refers to the ethical and transparent use of AI technologies to safeguard data and systems. It aims to make AI-driven decisions more explainable, fair, and free from biases. Responsible AI also means preventing misuse of AI by malicious actors.


